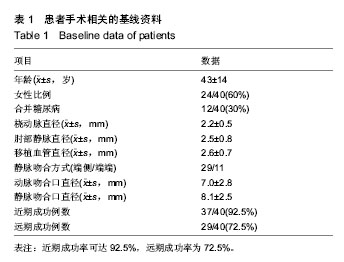
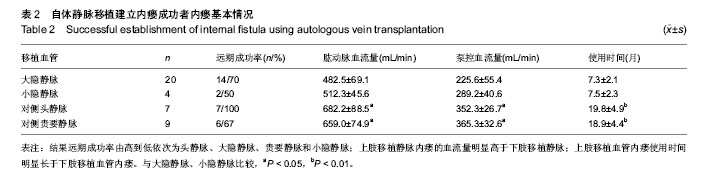
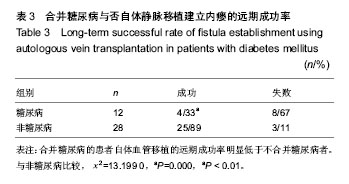
| [1] Gilpin V, Nichols WK. Vascular access for hemodialysis:thrills and thrombosis. J Vasc Nurs.2010;28(2):78-83.
[2] Anand S, Kurella Tamura M,et al. The elderly patients on hemodialysis. Minerva Urol Nephrol.2010;62(1):87-101.
[3] NKF-K/DOQI, Practice guidelines and clinical practice recommendation, 2006 updates.AJKD.2006;48;S5-S22.
[4] 中国医院协会血液净化中心管理分会血液净化通路学组.中国血液透析用血管通路专家共识(第1版)[J].中国血液净化, 2014, 13(8):549-558.
[5] National Kidney Foundation: K-DOQI clinical practice guidelines for vascular access. Am J kidney Dis.2006;48 Suppl l: 248-273.
[6] 安茂竹,孙静,张宏,等.前臂贵要静脉转位建立血管内瘘的临床应用[J].中华显微外科杂志,2010,33(4):343-345.
[7] 王蕴若,王惠新,吴昊,等.微创下前臂贵要静脉转位动静脉内瘘成形术[J].中华肾脏病杂志,2013,29(11):849-850.
[8] 褚志强.前臂头静脉转位与肱动脉吻合建立自体动静脉内瘘[J]. 中华普通外科杂志,2013,28(10):808-809.
[9] Besarab A, Sherman R.The relationship of recirculation to access blood flow. Am J Kidney Dis.1997;29:223-229.
[10] Wiese P, Nonnast-Daniel B.Colour Doppler ultrasound in dialysis access. Nephrol Dial Transplant.2004;19: 1956-1963.
[11] Leivaditis K, Panagoutsos S, Roumeliotis A, et al. Vascular access for hemodialysis: postoperative evaluation and function monitoring. Int Urol Nephrol.2014;46: 403-409.
[12] 叶朝阳.血液透析血管通路技术与临床应用[M].2版.上海,复旦大学出版社, 2010:85-86.
[13] 王玉柱,杨涛,任树风,等.自体股部大隐静脉移植内瘘临床应用分析[J].中国血液净化,2011,10(9):471-473.
[14] Reddan D, Klassen P, FranMield, et al. National profile ofpractice patternsfor hemodialysis vascular access in the united states. J Am SocNephrol.2002;13(8): 2117-2118.
[15] Oto T. Endoscopic saphenous vein harvesting for hemodialysis vascular access creation in the forearm: A newapproach for arteriovenous bridge graft. J Vasc Access. 2003;4(3):98-101.
[16] 岳勇,姚永杰,王冰.静脉顺应性的影响因素及测量方法[J]. 医用生物力学,2003,18(2):120-123.
[17] Kaufan JS, OconnorTZ , Zhang JH, et al.Randomized controlled trial of clopidogrel plus aspirinto prevent hemodialyaisaccess graft thrombosis. J Am SocNephrol. 2003;14( 9) :2313-2315.
[18] 李月红,于仲元,王玉柱,等.自体动静脉内瘘在血液透析中的应用[J].临床内科杂志,2003,20(8):408-409.
[19] Gaddi A, GalettiC,MumiutiB,et al.Meta-analysis of some results of clinical trials on sulodexide therapy in peripheralicclusive arterial discases.JInt Med Res. 1996; 24(3):389-390.
[20] Gefen JY, Fox D, Giangola G, et al. The transposed forearm loop arteriovenous fistula: a valuable option for primary hemodialysis access in diabetic patients. Ann Vasc Surg. 2002;16(1):89-94.
[21] Kim YO,Song HC,Yoon Sa,et al.Preexistiong intimal hyperplasia of radialartery is associated with early failure of radiocephalicarterioven-ousfistulain hemodialysis patients. Am JKidney Dis.2003;41(4):4228-4229.
[22] Schaper N, Houben A, Schoon Y, et al. Venous compliance and the venodiolatory effect of nitroglycerin in insulin-dependent diabetic patients with and without (incipient) nephropathy. Eur J Clin Invest.1994;24:382-387. |